 |
|
|
|
||
|
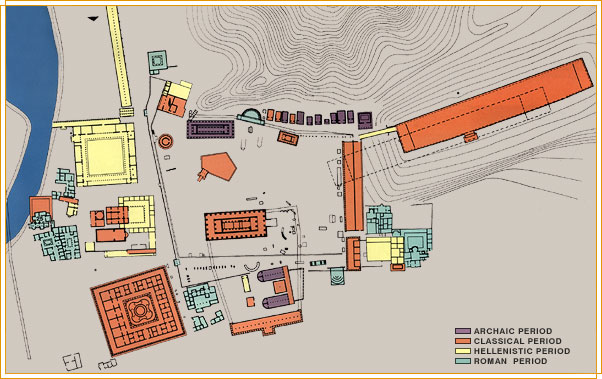
Topography of Ancient Olympia |
|||
|
|||
|
Treasuries The Treasuries were small temple-shaped structures built on a terrace inside the Altis and covered almost the entire north side of the sanctuary near the Cronios hill. The majority of these buildings dates from the 6th century BC and their construction is most likely related with the occupation of Pisa by the Eleans in 570 BC -who have greatly supported the growth of the sanctuary-, but mainly with the economic development of the Greek cities during the same period. These Treasuries housed the valuable votive objects that the cities offered to the sanctuary, hence their name. The votive objects included gold and ivory items, as well as vessels made of precious metals. Although Pausanias reports the existence of ten Treasuries, the excavations in the Altis brought twelve such buildings to the light. It is believed that the first Treasury belonged to Sikyon. Next followed the Treasuries of Syracuse, Epidamnus, Byzantium, Sybaris, Cyrene, two unidentified buildings, Selinus, Metapontum, Megara and Gela. Those of Byzantium, Selinus and Metapontum were built during the Classical era. |
